17 Difference Between Animal cell And Plant Cell & Functions
The word “cell” originally comes from a Latin word that means tiny space rooms. This is one of the greatest discoveries of humankind in bioscience ever that took place in the year 1838 by two biologists named Schleiden and Schwann. At that time, humans get to know that all the living things in the world were made up of small units that later came to be known as cells.
Meaning
Animal cell and plant cell are categorized under eukaryotes as both have possessed the traits of the eukaryotic cell and i.e., one of the most common similarities that we found in these two.
- First of all, both animal cell and plant cell are defined as eukaryotic cells due to the nature of eukaryotes they possess within themselves.
- Secondly, most of the plants are multicellular and less variety is found of unicellular. Animals are too unicellular and multicellular, containing millions and trillions no. of cells in a single being.
Animal Cell
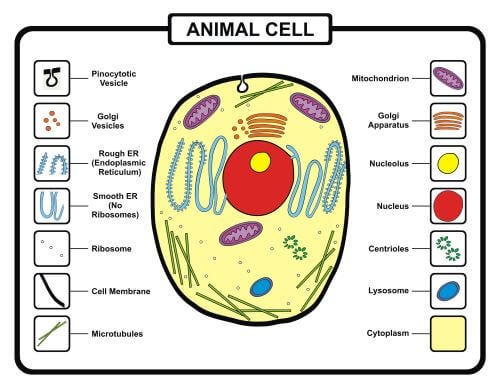
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum is further divided into two parts, namely smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum. They play a vital role in providing support to the animal cell to synthesize and process food within it in the form of mainly lipids and proteins.
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria is one of the important cell organelles in the animal cell as the functions and roles it plays are so needed to maintain the animal cell regimes. Moreover, it is the so-called powerhouse of the cell as it generates and stores energy in ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- Plasma Membrane: The plasma membrane is one such thin outermost protective layer that protects the cell from any external infection and germs entering the cell. As it allows entry and exit of any substance or molecules from or into the cell and, i.e., one of the reasons the name knows it of the selectively permeable membrane.
Plant Cell
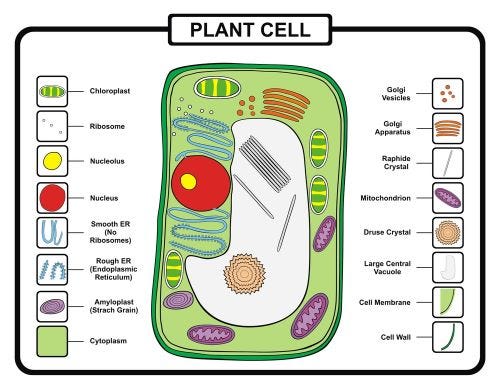
- Cell Wall: The cell wall is the thickened external layer of the plant cell that provides rigid support to the cell, and it is the primary protective covering that comes before the cell membrane. The cell wall is also responsible for providing shape and size to the cell. It is made up of the complex substance cellulose.
- Plastids: Plastids are the term that is used as a whole form for chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts in which chloroplast are one of the important plastids which contain the green-colored pigment chlorophyll. In contrast, chromoplasts are mostly light yellow, and leucoplasts are colorless. Chloroplasts help manufacture the food in the plant cell under the presence of sunlight by the process of photosynthesis.
- Vacuole: There is only one vacuole present in the plant cell, which is extremely large so that it covers the larger part of the plant cell. Vacuoles are bounded to the membrane and are sacs like structure which stores fluid and solid contents. Many major substances like sugar, proteins, and amino acids which are important in multiple plant life stages, are stored in vacuoles.
click here to continue
For More knowledgeable content, Contact Us on our website

Comments
Post a Comment